Asilia’s Role in Preserving Biodiversity
Biodiversity Loss Is Everyone’s Problem
“When we try to pick anything out by itself, we find it hitched to everything else in the universe,” said the 19th Century naturalist, John Muir.
Inverting that sentiment implies that eradicating just one species has a domino effect on multiple others. And so, the preservation of biodiversity has been allocated a day of recognition by the United Nations. Its purpose is to promote biodiversity issues.

The critical role of biodiversity in sustainable development was recognized at the Rio+20 Conference. Biodiversity impacts sustainable agriculture; desertification, land degradation and drought; water and sanitation; health and sustainable development; energy; science, technology and innovation, knowledge-sharing and capacity-building; urban resilience and adaptation; sustainable transport; climate change and disaster risk reduction; oceans and seas; forests; vulnerable groups including indigenous peoples; and food security.
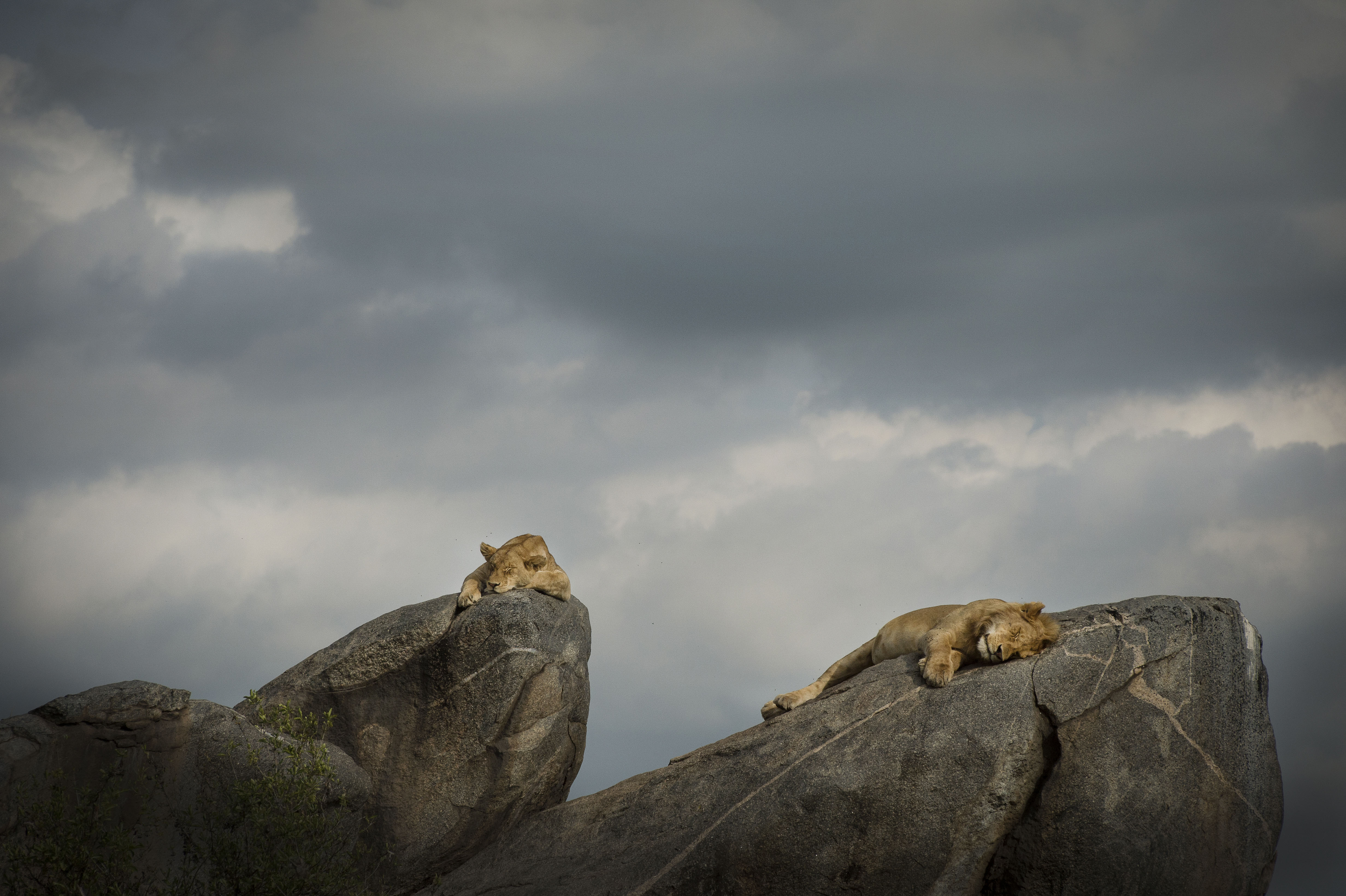
Asilia plays an important role in preserving biodiversity in some of the world’s last remaining wildernesses.
Ecosystems & Areas
Asilia has an area approach to positive impact. This means we look at the core wilderness areas where our camps are located, and the buffer zones and corridors that sustain them. For example, the Masai Mara and Northern Serengeti ecosystems are dependent on the Mara River, which arises in the Eburu Forest many kilometres away. Protecting the source, and the corridor that the river runs through, is vital to the continued existence of the Mara/Serengeti ecosystem. We contribute to a public-private partnership that protects the forest.
We take a similar approach in all the other areas we operate, where consideration for people and nature are equally important.
Keystone Species
In those ecosystems we also look at keystone species which are species that help define the ecosystem. These species are often, but not always, predators as their health is frequently indicative of the health of the underlying eco-system. At the top of the food chain, apex predators are often a good way to gauge the strength of the environment upon which they depend.
Many of the projects that Asilia supports relate to predators. Kenya Wildlife Trust monitors predators in the Masai Mara area, African People and Wildlife mitigates human-wildlife conflict especially with regards to predators, as does the Ruaha Carnivore Programme. All of these projects have predators at their core.
Humans
In East Africa, where many people are subsistence farmers and the increase in demand for agricultural land encroaches onto wilderness areas, we help in a variety of ways: from primary and secondary education support, tertiary scholarships to career opportunities. We believe that empowering people enables them to find alternative livelihoods to subsistence farming and poaching.
By staying with Asilia you contribute to preserving the world’s biodiversity.
More Positive Impact Articles

Electric Vehicles: The Future Of East African Safari Travel?
12 January 2020October 2019 saw the arrival of our first electric, solar-powered safari vehi...

Its Our 15th Birthday: Celebrating 15 Years of Making a Genuine Difference
08 November 2019This year, we're celebrating our 15th birthday and commemorating 15 years of...

World Tourism Awards 2019: Asilia Recognised For Our Positive Impact
01 November 2019The World Tourism Awards acknowledge, reward, and celebrate excellence across...

Supersized Traditional Maasai Necklace
21 October 2019In 2009, we became a founding member of the Mara Naboisho Conservancy and sin...