About Leopards
Leopards (Panthera pardus) are agile and adaptable. Known for their striking spotted coat and unique tree-top eating habits, they're one of the more threatened cats worldwide. While leopards are widely distributed across Africa and Asia, their populations are becoming increasingly reduced and isolated. Leopards have vanished from a vast portion of their historic range.
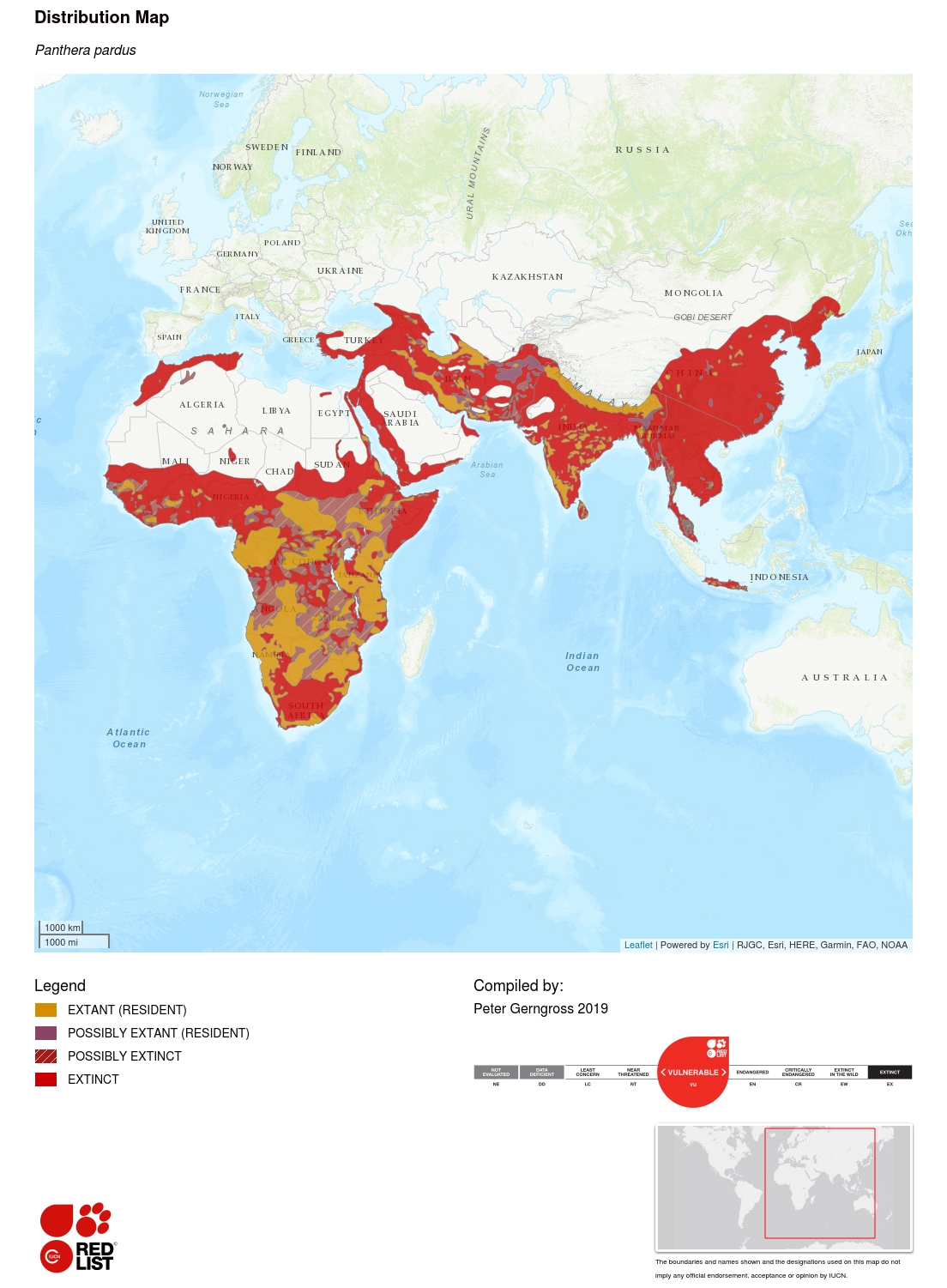
Leopard populations have vanished from their historic range in Eurasia, with a decline of up to 84%. In Africa, their range is almost two-thirds that of their historic range.
Distribution
Conservation Status
According to the IUCN, leopards are a vulnerable species. The overall population trend is decreasing.
The greatest threat to leopards is anthropogenic. Human-wildlife conflict over the livestock, habitat fragmentation due to changing land use, and a reduced prey base contribute to reduced leopard populations.
Habitat and Ecology
Leopards are found in a wide variety of habitats. Populations can be found in desert and semi-desert regions like Namibia and Botswana in southern Africa, areas in Egypt in North Africa, and the Arabian Peninsula.
These cats are known for roaming the savannah plains of East and southern Africa and the montane regions of southwest Asia in Iran and India. Populations have been found at elevations exceeding 4600m, like on Mt Kenya and even in the Himalayas. The forest and rainforest populations of leopards are located in West and Central Africa, Sri Lanka, and Southeast Asia.
Leopard diets can vary greatly depending on prey availability and competition from larger species. Traditionally, leopards prefer to prey on medium-sized, but they can also thrive on a diet that might include insects, reptiles, birds, and small mammals.
It’s common for individual leopards to become specialists at hunting a particular prey item and will feed almost exclusively on this, switching to other prey only when necessary.
The most iconic leopard behaviour is their tendency to hide their kills under thick vegetation. During the dry season, when vegetation doesn’t provide adequate cover, they will drag their meal into the trees. This behaviour is usually seen in the males of the species and is a reaction to the presence of larger competitors.
Leopard home range size will vary on the prey availability in the area. Arid areas will see leopards ranging more considerable distances in response to lower prey numbers, while forested habitats usually show the smallest home range for leopards.
Read more about Leopards
 Blog
Blog
Ruaha: A Leopard or an Expat Jaguar?
Pietro Luraschi tells us about the beautiful Onca, who roams the plains of Ruaha. Rosettes are rosettes, but jaguars have very different pattern and shape of rosettes compared to a leopard. On a jagua…
 Blog
Blog
Leopard vs Warthog: An Unforgettable Encounter
The post Leopard vs Warthog: An Unforgettable Encounter appeared first on Asilia Africa.
 Blog
Blog
Leopard vs Cheetah : Can You Tell The Difference
How often do you mistake a leopard for a cheetah or vice versa? I’m sure we’ve all made this mistake once or twice.